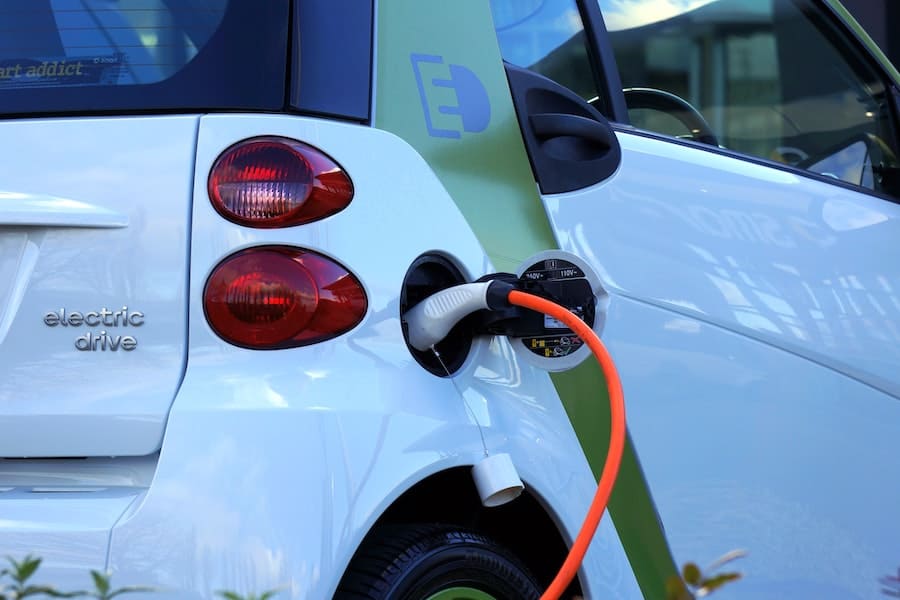
Electric cars have only recently become a regular sight on the roads of the world. All the major car manufacturers are looking to increase their electric vehicle (EV) fleet and make it as widespread as possible. But how can you be sure that an electric car has an authentic, working battery? With so many different makes and models of electric vehicles, you may wonder why some of them don’t have working alternators. After all, alternators are an essential piece of any car’s electrical system. Without them, your electric car won’t be able to charge its batteries or run its headlights and other electrical systems.
Why don’t electric cars have alternators?
Electric cars don’t have alternators because they don’t need them. Alternators are used in conventional gasoline-powered cars to generate electricity and recharge the car battery. However, electric cars have an entirely different powertrain; instead of using an internal combustion engine to generate electricity, electric vehicles use powerful batteries that store energy and distribute it to multiple motors for propulsion.
The Different Types Of Electric Car Alternators
1. Permanent Magnet Alternator:
A permanent magnet alternator utilizes a series of magnets that are stationary and generate an alternating current. This type of alternator is highly efficient, as the magnets can produce steady electricity with relatively little energy used in the process. Additionally, this system does not require any moving parts to operate, making it a reliable choice for electric cars.
2. Switched Reluctance Alternator:
This type of alternator is a bit more complex, as it uses varying levels of reluctance instead of magnets to generate an alternating current. It has no stationary parts but instead relies on a switch that changes the magnetic field every few milliseconds in order to produce electricity. While this technology is relatively efficient and reliable, it is also somewhat more expensive than other systems.
3. Induction Alternator:
An induction alternator uses a rotating magnetic field to produce electricity. The rotation of the field induces an electric current in the coils surrounding it. This type of system is able to generate higher levels of output but requires more energy in order to do so, making it less efficient than the other two types of alternators.
4. Synchronous Alternator:
This type of alternator utilizes a series of permanent magnets, along with some stationary coils, to generate an alternating current. Unlike the permanent magnet system, this one has fewer parts and requires less energy in order to generate electricity. While this is an efficient system, it is also more expensive than the other types.
5. Brushless Alternator:
A brushless alternator uses a combination of magnets and coils to generate electricity. This type of system is relatively efficient, but it also requires more energy in order to produce the same amount of power as the other systems. Additionally, this type of system is highly sensitive to temperature changes, making it less reliable than the other types.
6. Multi-Phase Alternator:
This type of alternator combines multiple phases in order to generate an alternating current. This system is very efficient and reliable, but it is also quite expensive. Additionally, this system requires more complex circuitry in order to operate properly.
7. Hybrid Alternator:
A hybrid alternator is a combination of multiple types of alternators, such as the permanent magnet, switched reluctance, and induction systems. This type of system can be tailored to meet specific needs, making it highly customizable and efficient. However, this type of system is also quite expensive and requires more energy in order to generate electricity than the other types.
How To Check Your Electric Car’s Battery?
- Once you have the tools or equipment needed, you can begin to check your electric car’s battery. Start by plugging in a multimeter, or similar device, into the charger port of the vehicle. Make sure that you are using a digital display to get an accurate reading.
- Next, turn on the multimeter and adjust the settings to read “Battery Volts.” This will give you an indication of the total amount of charge in the battery.
- If the reading is between 12-14 volts, then it means that your electric car’s battery is fully charged and working properly. However, if it reads less than 12 volts, then the battery may need to be recharged.
- Once you get the readings, make sure that you keep an eye on them over time. This will help you determine whether or not there is a problem with your electric car’s battery that needs to be addressed. If the reading does not improve after charging, then it might be best to take your vehicle to a professional.
- Lastly, make sure that you keep track of any maintenance and repairs performed on your electric car’s battery. This will help you ensure that the battery is working properly and that it has been adequately taken care of over time. Keeping up with regular maintenance checks can help prolong the life of your battery and keep your electric car running smoothly for years to come.
- Remember, if you ever feel uncomfortable performing these steps yourself, it’s best to consult with a professional mechanic or technician who has experience in checking the battery of an electric car. They will be able to tell you the exact condition of your battery and offer advice on how to best maintain and care for it. With a little bit of effort, you can be sure that your electric car’s battery is working properly and safely at all times!
The Difference Between A Battery And An Alternator
- A battery is a device used to store and supply electrical energy, while an alternator is a device that produces electrical energy. The battery stores the power generated from the alternator, which is, in turn used to power your vehicle’s motor.
- Batteries are typically composed of lead plates, sulfuric acid, and distilled water. These components react with each other and store energy in the form of chemical energy. The alternator is most commonly powered by a belt driven by the crankshaft pulley, although some vehicles use direct drive systems.
- The primary difference between a battery and an alternator lies in their purpose: the alternator is used to create power while the battery stores it.
- The battery and alternator are both essential components of an automobile’s electrical system, working together to provide the necessary power for vehicle operation. The alternator is responsible for creating a charge from the engine’s rotation that can be stored in the battery, while the battery is responsible for providing power to the vehicle’s electrical components.
- When a car has been idle for an extended period of time, the battery will eventually become drained due to its lack of use; this is why it’s important for drivers to regularly start their cars and allow them to run for a few minutes. This will ensure that the alternator is able to recharge the battery and provide it with enough stored power to operate properly.
Summary
The best option for an electric car is one that has a good battery and an effective alternator. Make sure the car has an authentic, working battery and an effective alternator. If your car doesn’t have either, then your electric car won’t be as powerful as it could be. In addition, make sure that the car you choose has the features you want in your electric car, such as a comfortable seat, plenty of room for your gear, and quick charging capabilities.


















Leave a Reply